Context and issues
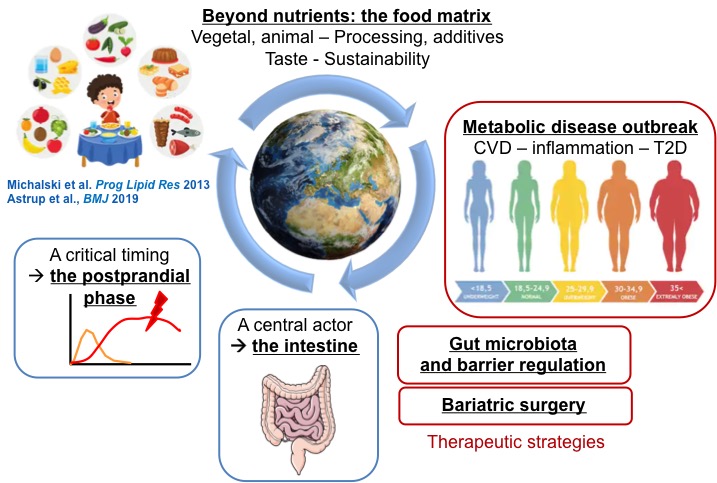
Nutrition is a major environmental risk factor for metabolic diseases (such as obesity and type 2 diabetes) and their complications (cardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic kidney failure, etc.). In addition, we are facing an unprecedented environmental crisis that raises key new sustainable food issues with the goals of optimal nutrition and population health.
In this context, the intestine is clearly a central actor in the link between nutrition and metabolic diseases, through the absorption of nutrients, regulation of the postprandial phase, bile acid metabolism, modulation of the intestinal microbiota, and fine control of specialized cells related to the gut barrier integrity and the production of gut hormones.